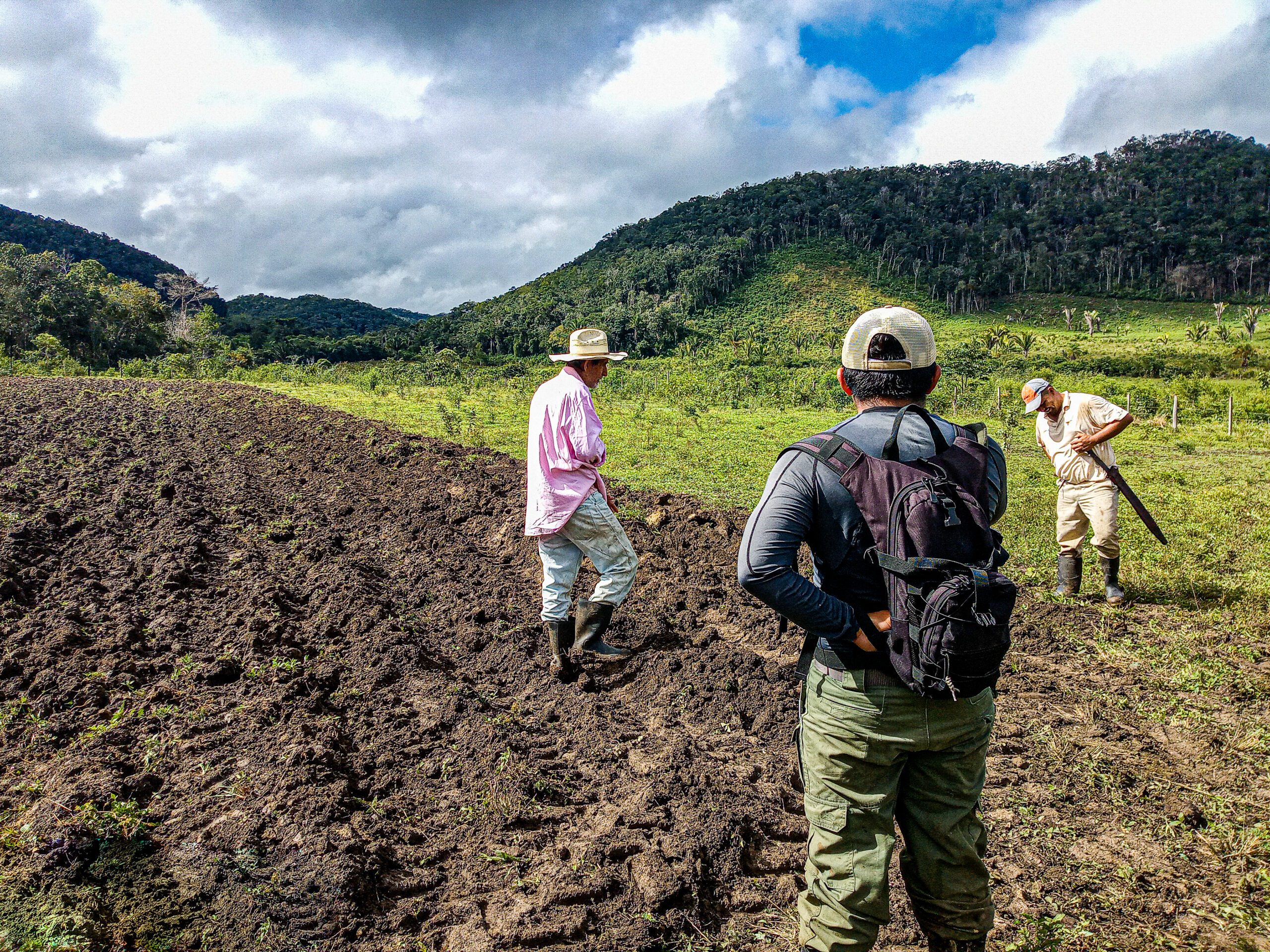
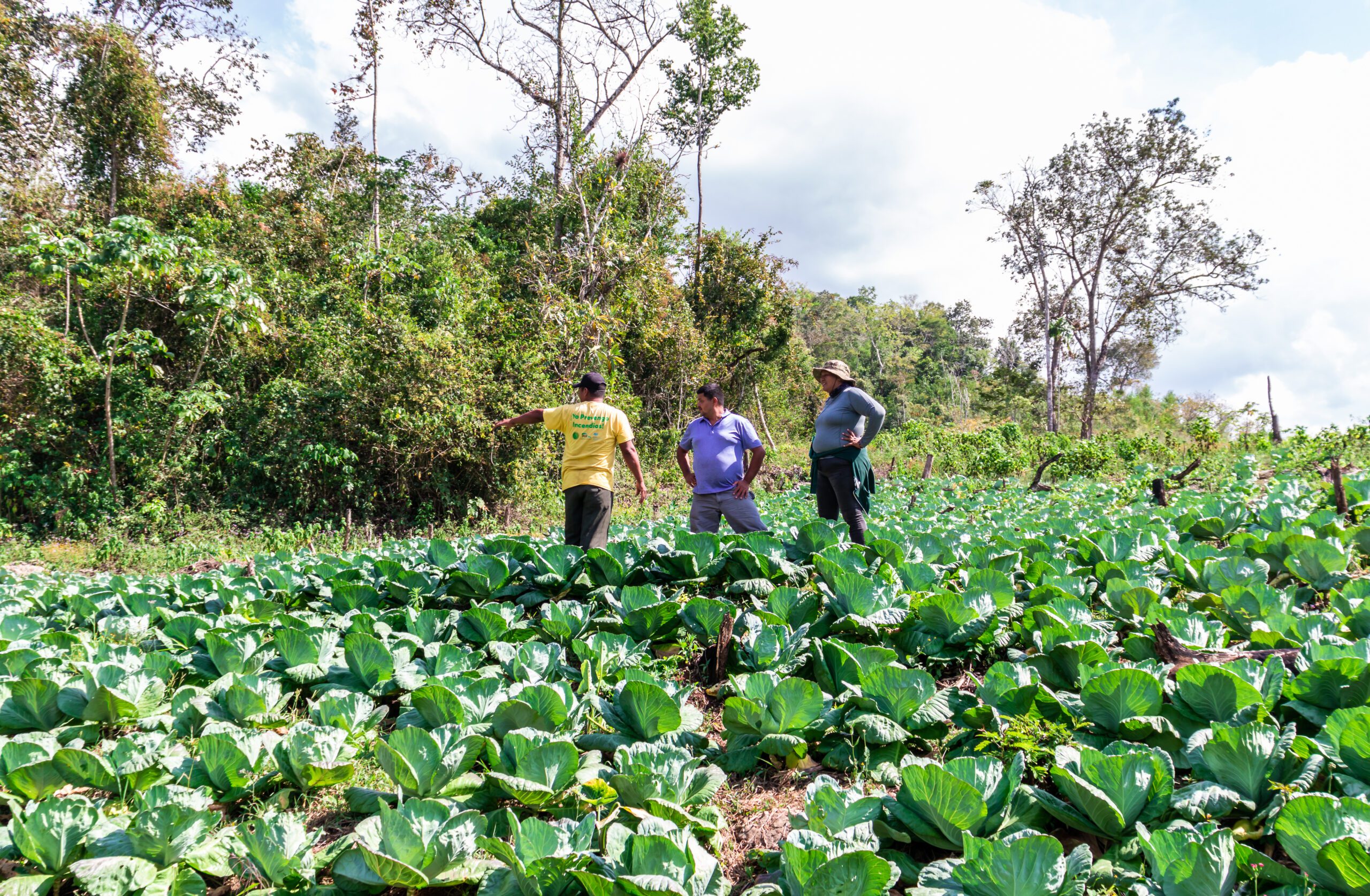
The Vaca Forest Reserve borders the northern flank of the Chiquibul National Park. Since 2010 with a request from the Forest Department, FCD developed a Landscape Management Strategy aimed at incorporating local community members to participate in the restoration, protection, and production of the forest reserve. Since then, over 20 of these farmers, known as the Friends of the Vaca Forest Reserve have been the center of an adaptive management strategy that uses integrated farming methods and climate smart agro-ecological systems.
The Vaca Forest Reserve continues to function as a key buffer for the Chiquibul National Park and continues to contribute to the functioning of the Belize River watershed whilst maintaining its intrinsic natural values and contributing to local development.
The Vaca Forest Reserve (VFR) is bordered in the north by the villages of Arenal and San Jose Succotz and the small town of Benque Viejo del Carmen. The zone between the VFR and the communities is a mixture of farmland and forested land, the latter mostly secondary growth in various stages.
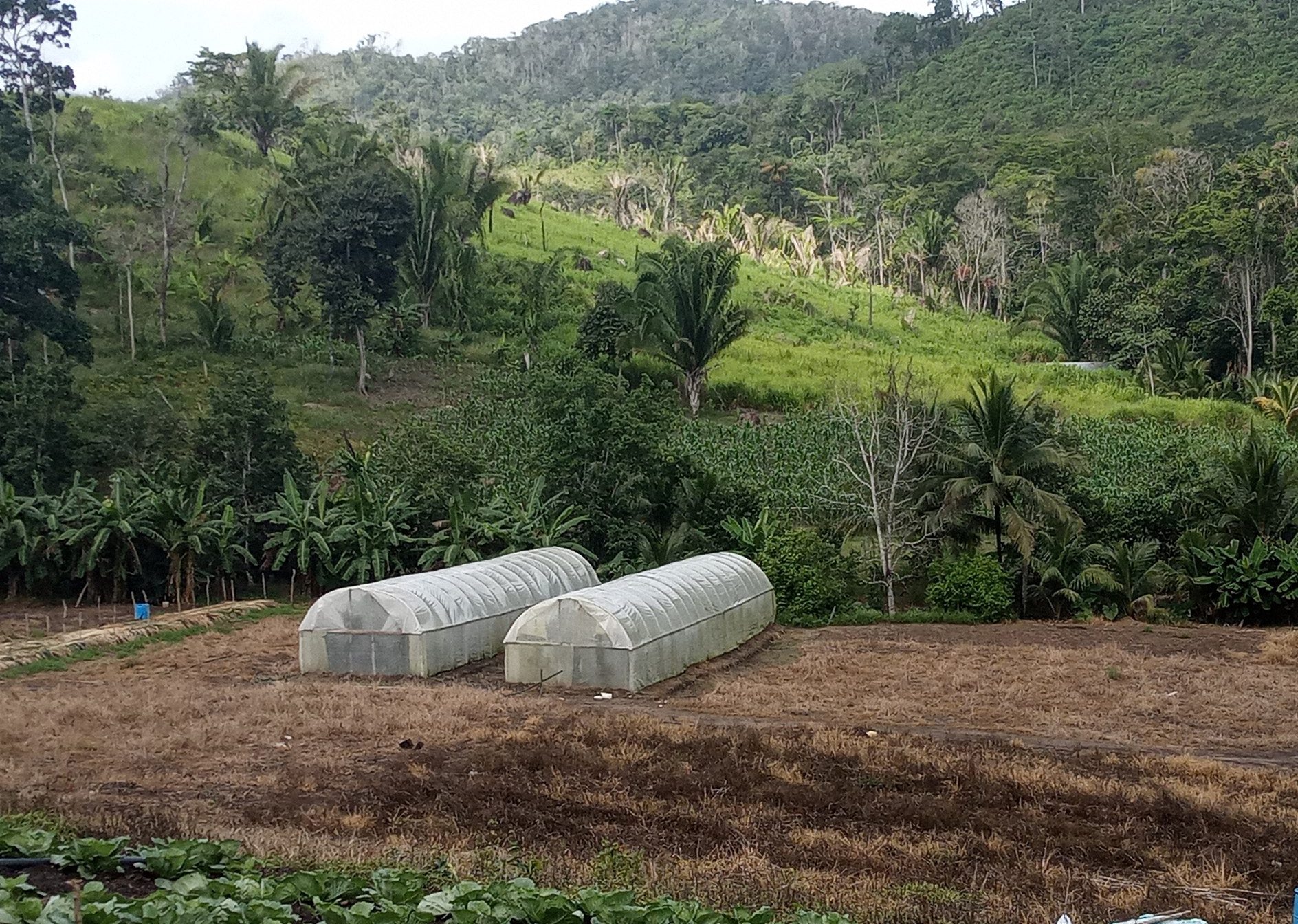
The dominant land use in the VFR is crop agriculture, which can be observed by the cultivation of crops as well as a growing cattle ranching activity in adjacent areas. Due to the limitations of the terrain, mechanized farming is not prominent in the area, although small machinery is used to prepare suitable soils for the growing of crops. Agriculture encroachment occurs in three main areas, the eastern block, the northwest block, and in the southwest (an area close to the boundary line with the CNP).
A baseline study conducted by FCD in 2017, documented a total of twenty-one (21) farmers within the boundaries of the eastern section. The baseline study noted that 47.6% of the farmers inside the reserve claimed about 1-25 acres of land, while 23.8% of the farmers claimed about 26-50 acres, 14.3% of the farmers claimed 51-100 acres and 14.3% of the farmers claimed more than 100 acres of land inside the VFR.
The most common type of agriculture use in the Eastern Section of the VFR was vegetable production (47.6%), followed by mixed farming of fruit and vegetable production (28.6%), only fruit production (19.0%), and finally by cattle ranching (4.8%). This indicated that farmers, on average, were operating small productive plots of land to produce vegetables and that cattle ranching was uncommon within the eastern section of the reserve.
FCD’s Extension Technician works closely with farmers and cattle ranchers near the reserve, promoting agroecological methods that can help reduce land, forest and water degradation.
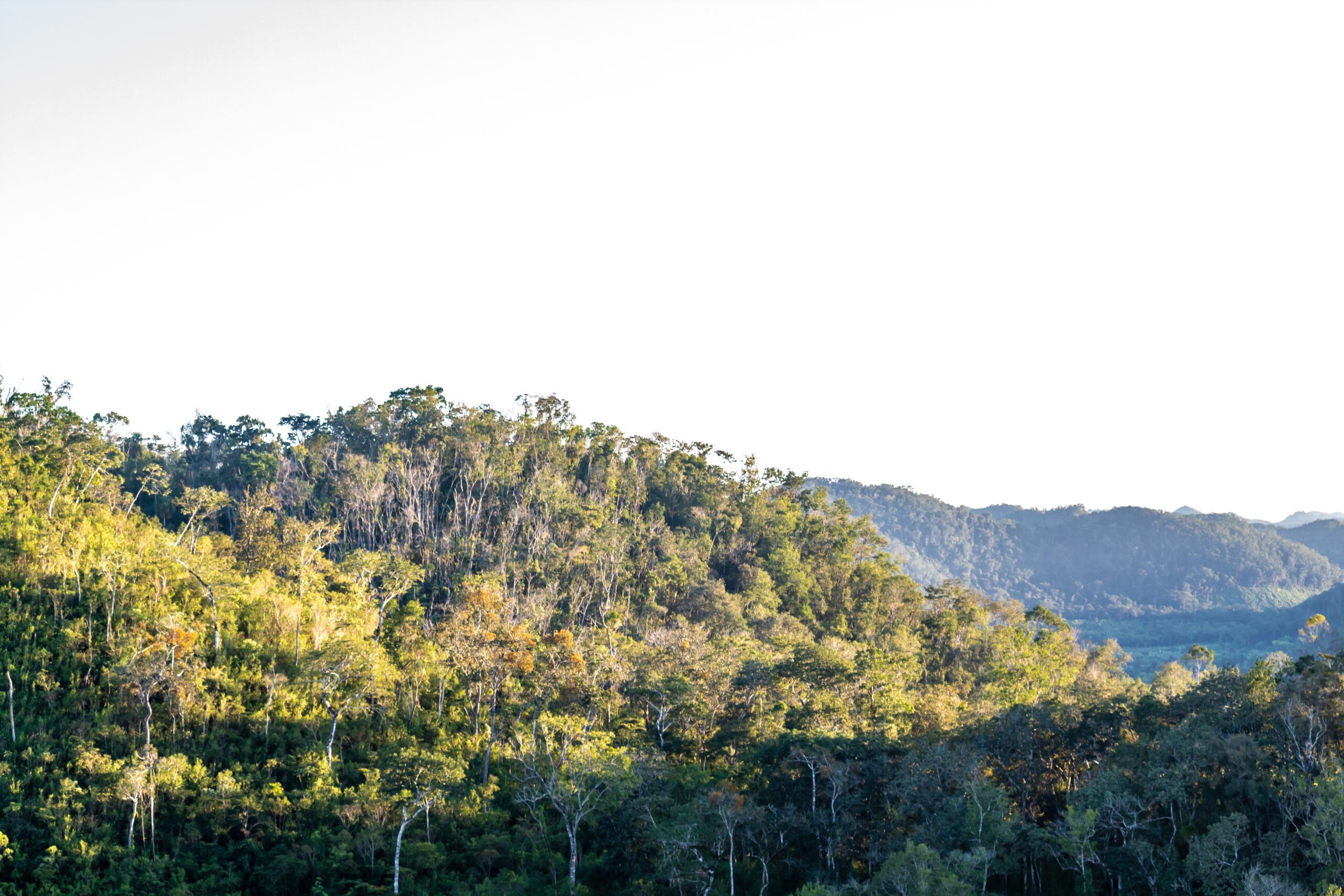

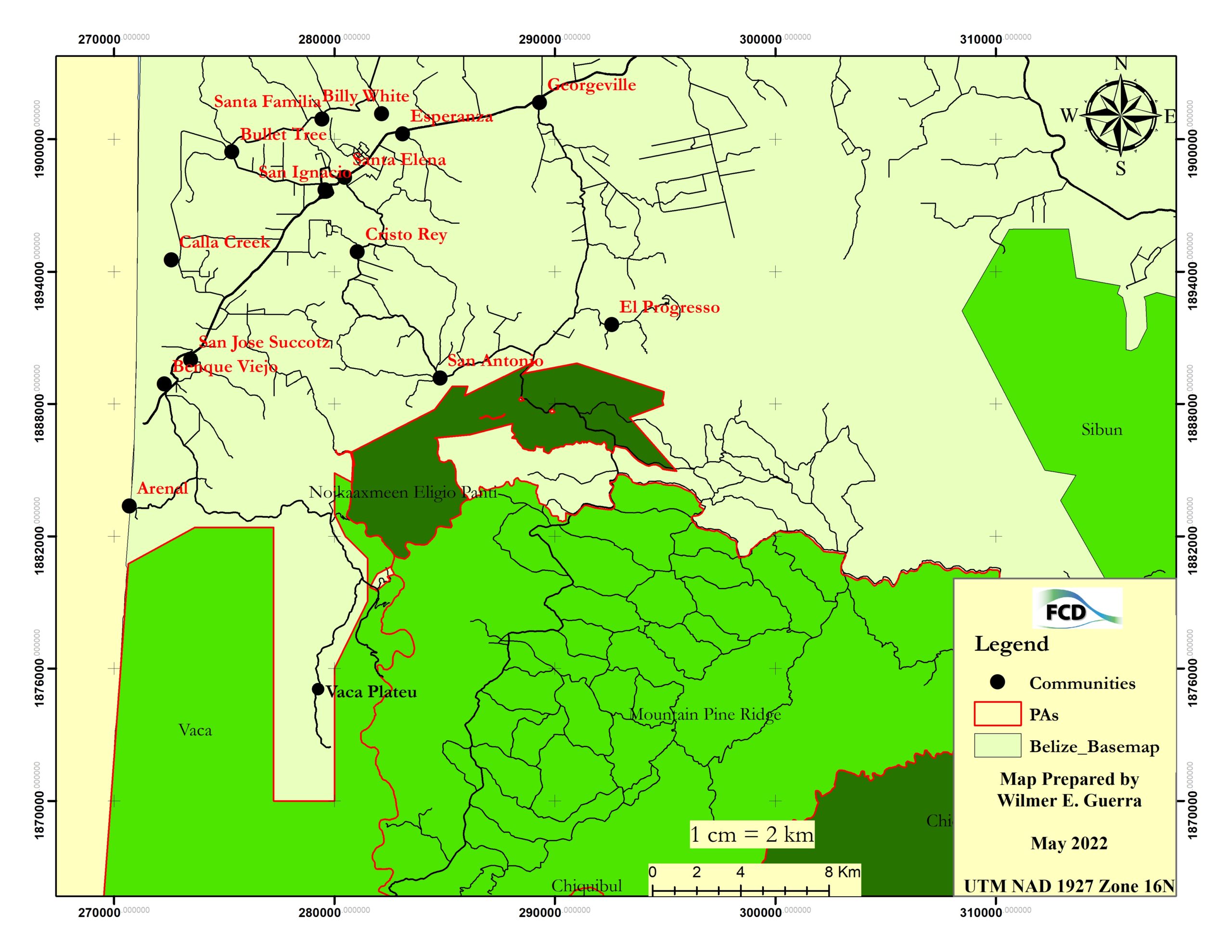







The Vaca Forest Reserve (VFR), managed by the Belize Forest Department (FD) is located in western Belize and forms part of the Chiquibul Maya Mountain Massif. The VFR is bordered on the east by two protected areas, namely the Mountain Pine Ridge Forest Reserve and the Noj Kaax Meen Elijio Panti National Park, to the south by the Chiquibul National Park and to the west by Guatemala. To the north, the reserve is bordered by government lands which are primarily being used for agricultural development. The VFR is one of the first five protected areas to be declared in Belize during the early 1930s. The reserve boundaries were re-defined in 2003, leaving a total of 40, 313 acres. The forest fires of 2020 and 2023 have heavily impacted the reserve, which will require heavy investments in finance and labor to recover the Vaca landscape.
Chi-Hah Street, San Jose Succotz
Cayo District, Belize